Systematic Cloud Microphysics Scheme Development with Machine Learning
Submitter
Lamb, Kara Diane
— Columbia University
Area of Research
Cloud Processes
Journal Reference
Lamb K, C Singer, K Loftus, H Morrison, M Powell, J Ko, J Buch, A Hu, M van Lier Walqui, and P Gentine. 2025. "Perspectives on Systematic Cloud Microphysics Scheme Development with Machine Learning." Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, 18(1), e2025MS005341, 10.1029/2025MS005341.
Science
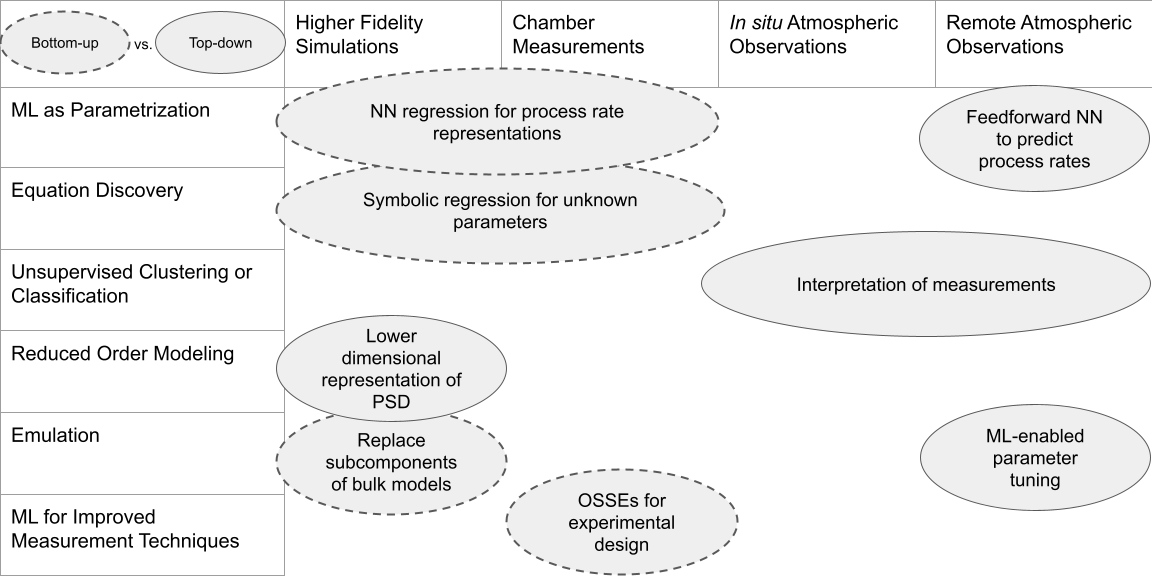
Examples of data-driven approaches applied to bottom-up or top-down cloud microphysical scheme development, categorized by method and data source.
Cloud microphysics refers to the microscale processes that impact liquid droplets and ice crystals in clouds and precipitation. Because of uncertainty in both cloud microphysical processes and in how these processes should be represented in models, they are a major source of uncertainty in current weather and climate models. The recent application of machine learning (ML) methods to atmospheric model development holds significant promise to address current limitations in modeling cloud microphysics and thus improve atmospheric models. In this perspectives paper, we discuss both challenges and future opportunities in applying ML methods to cloud microphysics.
Impact
Cloud microphysical parameterization remains a major challenge, limiting the accuracy of weather and climate models. Motivated by rapid progress in using ML in the atmospheric sciences, our paper highlights the special challenges and opportunities of applying ML to cloud microphysics scheme development. While recent papers have explored ML-based parameterization development for weather and climate models, the application of ML to cloud microphysics has remained limited, despite its importance for weather forecasting and climate projections. We argue that this is owing to the unique challenges of parameterizing microphysics. Arising out of discussions with researchers at the Learning the Earth with Artificial Intelligence and Physics (LEAP) Center, our article summarizes these challenges, evaluates recent progress using ML, and highlights opportunities for future breakthroughs.
Summary
In this perspectives paper, we review recent progress in using data-driven approaches and ML to improve cloud microphysics parameterizations. The most recent work has focused on supervised learning of high-resolution or high-fidelity simulations. We discuss both the challenges and additional opportunities for combining ML approaches with observations and models of cloud microphysics and for developing unified cloud parameterizations that combine cloud microphysics, turbulence, and large-scale cloud processes. Addressing the uncertainties of cloud microphysics (incomplete physical understanding, imperfect numerical representation, and uncertain spatiotemporal scale dependence) requires a better integration of models and observations and more systematic scheme development. We also emphasize several research areas where the cloud microphysics community can make significant progress in the coming years: developing large-scale benchmark data sets of in situ observations, integrating microphysics schemes in differentiable modeling frameworks that unify top-down and bottom-up constraints, designing unified parameterizations for cloud processes, and improving sampling strategies through observing system simulation experiments (OSSEs).
First, we briefly review current approaches to modeling cloud microphysics at different scales. Next, we discuss the core uncertainties and challenges for cloud microphysical scheme development. We then describe recent applications of ML to cloud microphysics and discuss how data-driven approaches can help address key challenges in parameterizing cloud microphysics. Finally, we conclude with perspectives on how the next generation of ML-enhanced cloud microphysical schemes can be developed by systematically leveraging observations, high fidelity models, and data-driven methods.
Keep up with the Atmospheric Observer
Updates on ARM news, events, and opportunities delivered to your inbox
ARM User Profile
ARM welcomes users from all institutions and nations. A free ARM user account is needed to access ARM data.


















