Research Highlights
Scientists and investigators using Atmospheric Radiation Measurement (ARM) User Facility data publish about 150 peer-reviewed journal articles per year. These documented research efforts represent tangible evidence of ARM’s contributions to improving our understanding of clouds and aerosols and their interactions with the Earth’s surface. ARM research highlights summarize these published research results.
Share your Research with ARM
Each of your DOE-funded journal articles should include a research highlight. This is an important opportunity to summarize your work and describe its scientific impact. ARM has a simple form for you to fill out to share your highlight with ARM management.
Explore the Highlights Database
Check out research highlights submitted by members of the ARM community and view each highlight’s linked journal article. Search the database by title, author, or research area.
Recent Highlights
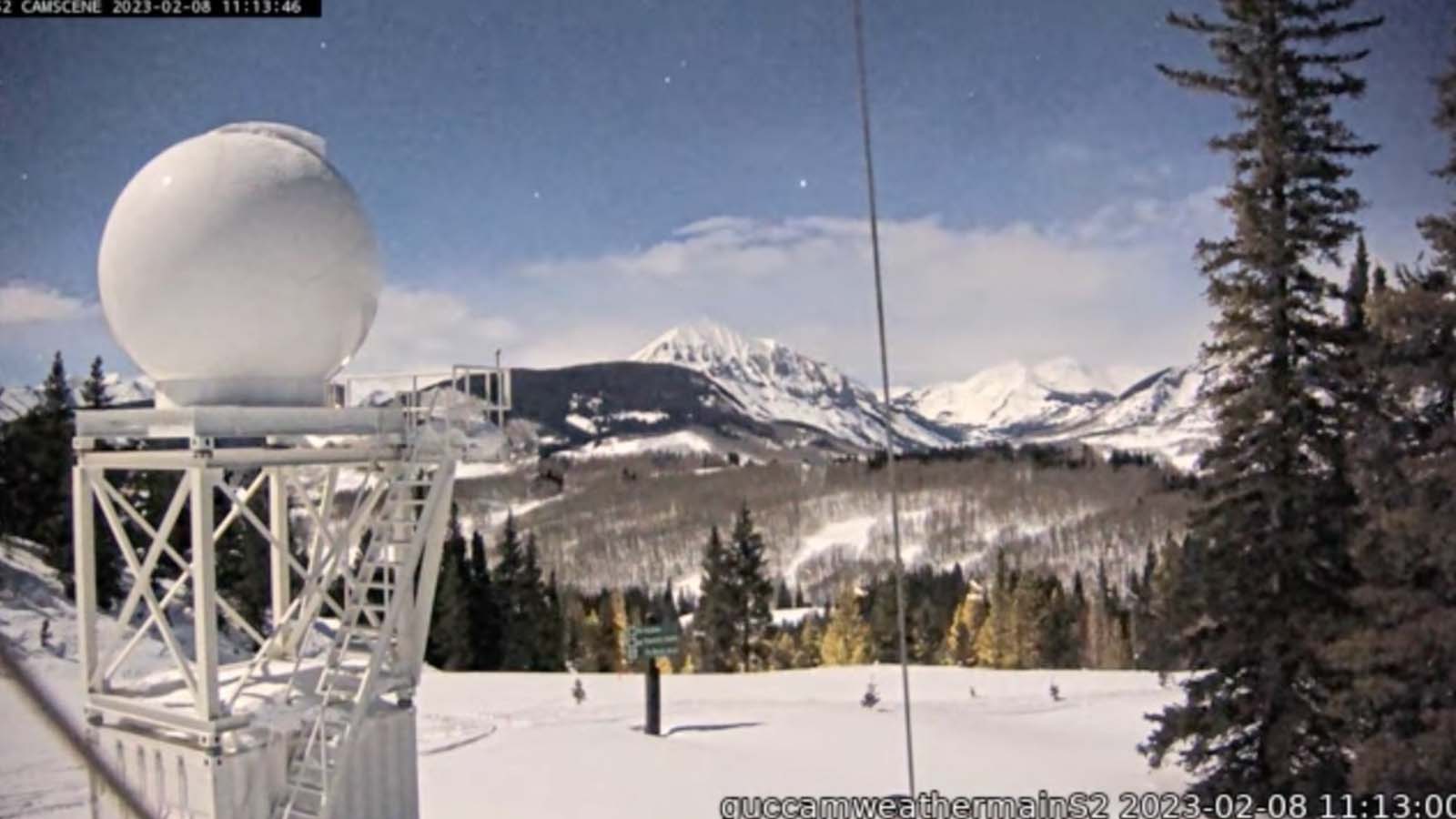
Significant Mountain-driven Snowfall Missed by National Weather Radars
16 February 2026
Hickmon, Nicki
Research area: Cloud Processes
ARM
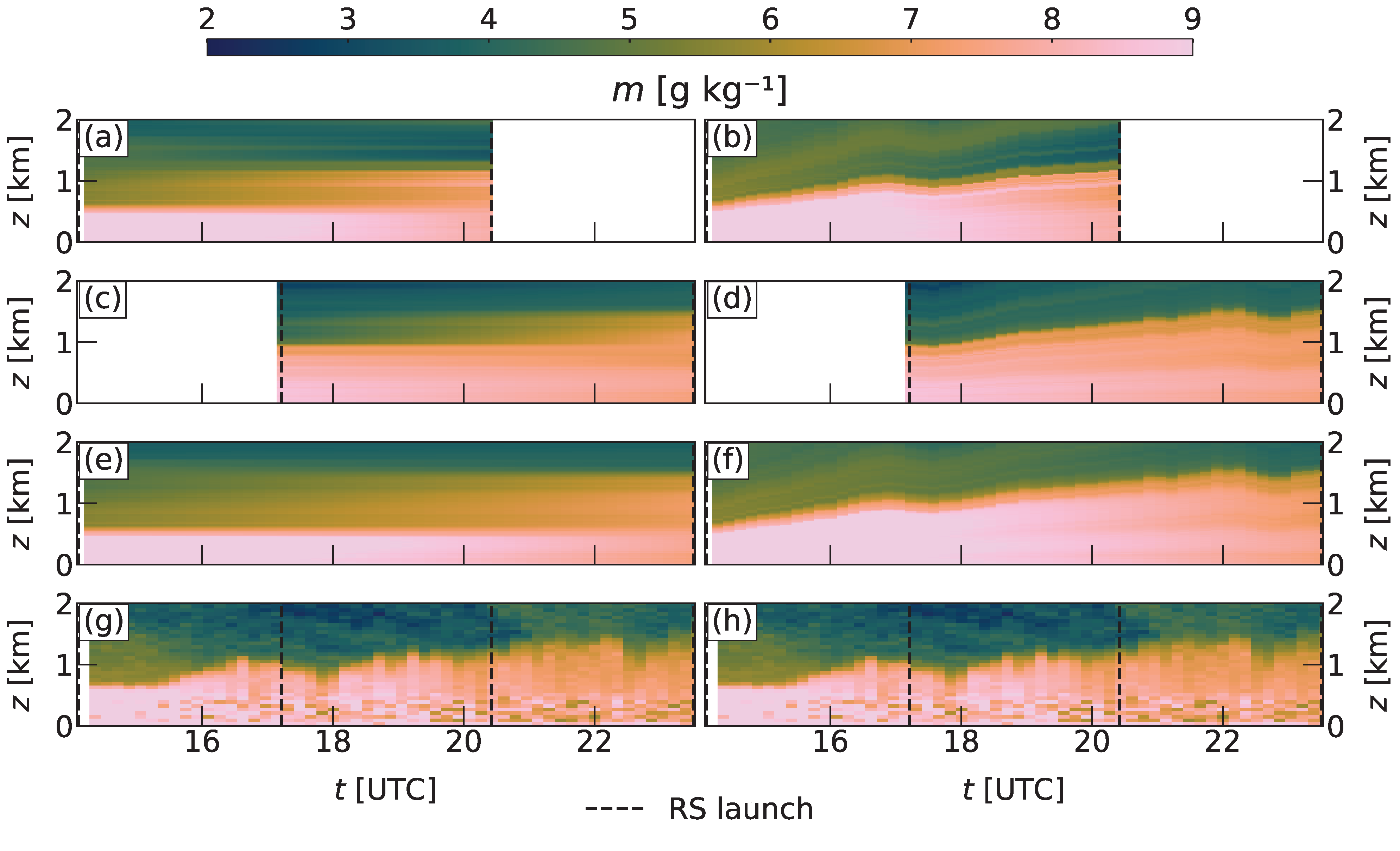
Improved Method to Temporally Interpolate Radiosonde Profiles in the Convective Boundary Layer
5 February 2026
von Klitzing, Linus; Turner, David D.
Research area: Atmospheric Thermodynamics and Vertical Structures
ARM
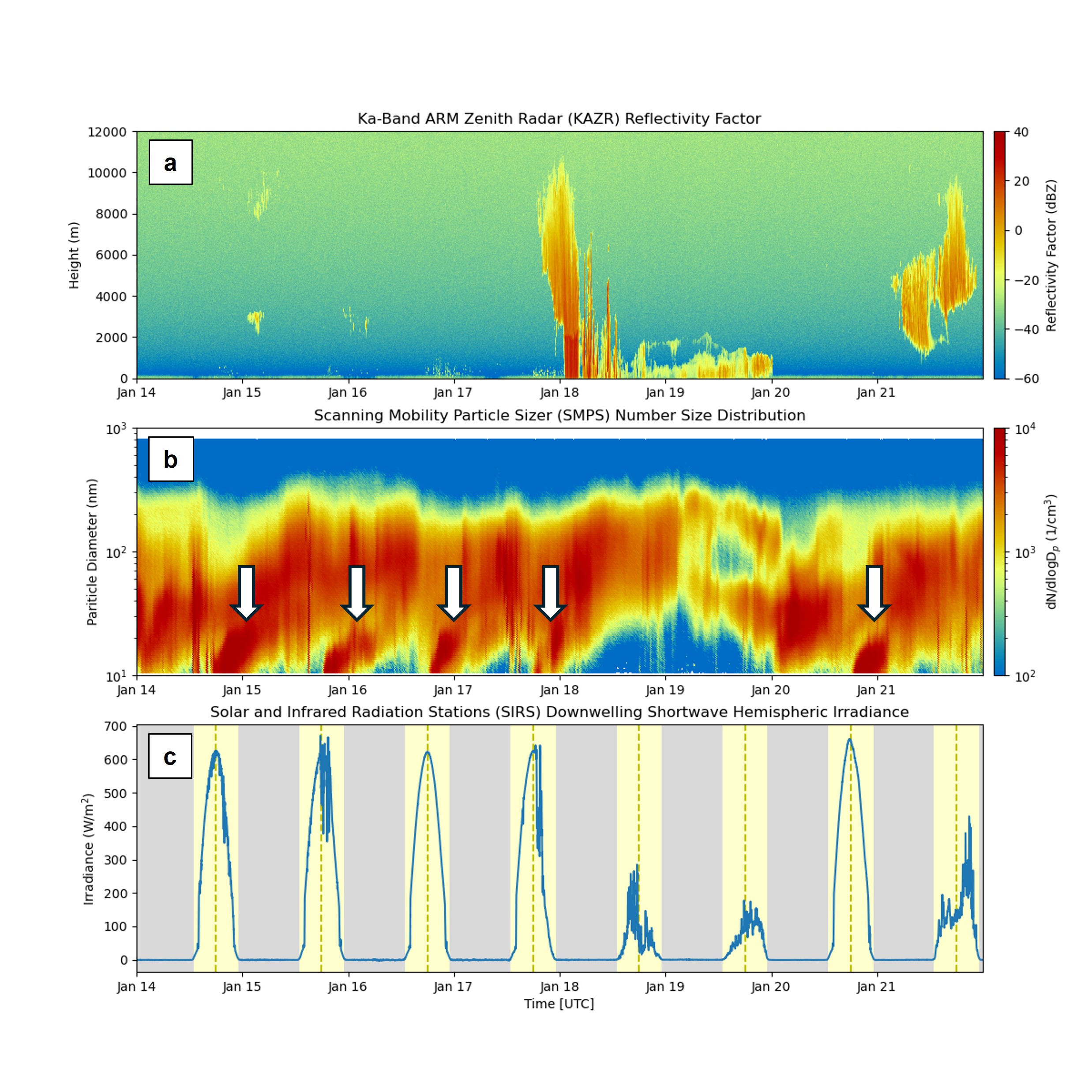
ARM Establishes a New Site for Studies of Land–Aerosol–Cloud Interactions in the Southeast U.S.
4 February 2026
Kuang, Chongai
Research area: Cloud-Aerosol-Precipitation Interactions
ARM ASR
Keep up with the Atmospheric Observer
Updates on ARM news, events, and opportunities delivered to your inbox
ARM User Profile
ARM welcomes users from all institutions and nations. A free ARM user account is needed to access ARM data.